Regular expressions allow you to find patterns in character combinations in a string. It's super powerful and are used in modern search engines and word processors.
There are three types of REGEX Function in Stackby. They are REGEX_MATCH(), REGEX_EXTRACT(), and REGEX_REPLACE(). All this are formula which has advantages and disadvantages depending on the formula output
In this article, we will learn the following Regular expression functions:
- REGEX_MATCH()
- REGEX_EXTRACT()
- REGEX_REPLACE()
1. REGEX_MATCH
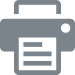
The REGEX_MATCH() function returns whether the input text matches a regular expression and outputs in the Boolean data type as a 1 as true or 0 as false result.
Example: Phone number validation and Email validation.
Phone No.: REGEX_MATCH( {Phone}, ‘^([+]?[0-9]( |-)?)?(\\(?[0-9]{3}\\)?|[0-9]{3})( |-)?([0-9]{3}( |-)?[0-9]{4}|[a-zA-Z0-9]{7})$‘)
Email: REGEX_MATCH({Email}, “(\\W|^)[\\w.\\-]{0,25}@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\\.[A-Za-z]{2,}(\\W|$)“)
2. REGEX_EXTRACT()
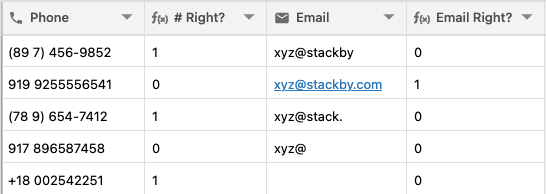
In the REGEX_EXTRACT() function it returns the first substring that matches a regular expression. If the REGEX_EXTRACT() function finds no matching instance of the provided regular expression it will return an ERROR.
Example: Extracting ID from a URL
Formula: REGEX_EXTRACT({URL}, “[^=]+$“)
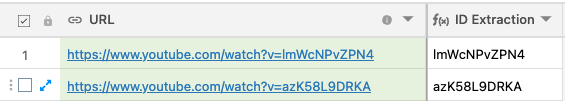
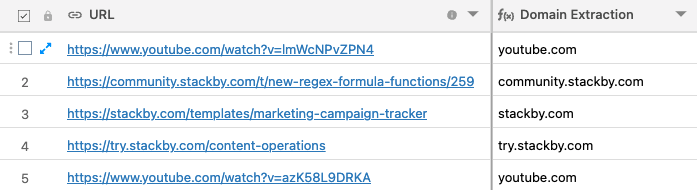
Another example: Domain Extraction from a URL
Formula:
REGEX_EXTRACT( {URL}, ‘^(?:https?:\\/\\/)?(?:[^@\n]+@)?(?:www\\.)?([^:\\/\n?]+)’)
3. REGEX_REPLACE()
The REGEX_REPLACE() function substitutes all matching substrings with a replacement string value.
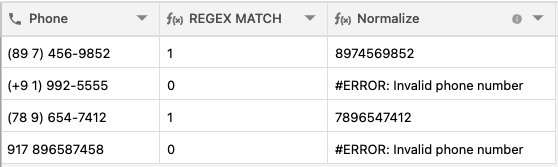
Let’s see if we have to normalize all our phone numbers in the table, we will follow the steps below:
We’ll first check if we have a valid phone number with REGEX_MATCH, then we can use REGEX_REPLACE to bring an output for a normalized phone number.
First use REGEX_MATCH: REGEX_MATCH( {Phone}, ‘^([+]?[0-9]( |-)?)?(\\(?[0-9]{3}\\)?|[0-9]{3})( |-)?([0-9]{3}( |-)?[0-9]{4}|[a-zA-Z0-9]{7})$‘)
Then use REGEX_REPLACE to normalize: IF({REGEX MATCH}, UPPER(REGEX_REPLACE( {Phone}, ‘[^A-Za-z0-9]‘, ‘’)), ERROR(‘Invalid phone number’))